ADVANCED PURATEK® STABILIZATION & SOLIDIFICATION TECHNOLOGY FOR HAZARDOUS SOLID WASTE AND NORM* WASTE TREATMENT
(* NORM: NATURAL OCCURING RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL)
The SOLIDIFICATION, also known under the terms STABILIZATION, IMMOBILIZATION or CONDITIONING, is a chemical and physical process, that encapsulates contaminants nonleachably and permanently and thereby minimizes the risk of environmental hazard.
Stabilization & Solidification procedures are aimed at producing a stable, landfill-disposable product with the lowest possible level of leaching. Here, the terms “stabilization” and “solidifi cation” are used. Deposition of stabilized hazardous waste at Class I and Class II Landfills is permitted only if “total stabilization” can be demonstrated.
One of the test criteria to prove the success of Stabilization & Solidification of hazardous solid waste is the TCLP (Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure) test method 1311 described in USEPA publication SW-846. The target values of the Stabilization & Solidification treatment are shown and summarized in table below:
Typical Target Values (product quality) of Stabilization & Solidification
By processing of NORM waste material, beside over mentioned criteria, additionally signifi cant reduction of radiation must be achieved, so that the fi nal product is acceptable for safe disposal on the special controlled low radiation waste depot.
The limits for disposal of processed NORM waste material are stipulated in the National Regulations that slightly differs in each country. PURATEK® advanced technology of NORM waste treatment provides fi nal product quality which complies with current best international practice.
Conventional Stabilization & Solidification of heavy metal contaminated chemo toxic hazardous waste using Portland cements or fl y ash is based on the presence of free CaO in cement, which is capable of forming insoluble or slightly soluble metal hydroxides with most metals.
The elements of the zinc group, cadmium and mercury: (Zn++, Ag++, Hg++, Cd++, Pb++, Cu++ and Ni++ in particular), are known to be exceptions to this rule; therefore, the respective sulphidisation of this metals prior to fixing (encapsulation) in a cement-stone matrix is essential.
Insolubility (or extremely low solubility) of the compounds to be solidified is indispensable for successful completion of the solidification process.
For this reason, a two-stage process is necessary.
The first stage provides for stabilization and precipitation of heavy metals. The second stage encapsulates the previously stabilized and precipitated contaminants into the crystal lattice or solid matrix of the final solidified product.
In the past 10 years, PURATEK® has developed advanced two-stage Stabilization & Solidification technology for successful treatment of hazardous solid waste and NORM waste, realizing the fact, that stabilization is a chemical process; therefore, the simple cementation in concrete mixing plant, cannot deal successfully with this task. The common and simple cementation of waste using concrete mixing plants is not purposeful and unsuitable to achieve proper solidification result.
Insolubility (or extremely low solubility) of the compounds to be solidified is indispensable for successful completion of the solidification process.
For this reason, a two-stage process is necessary.
The first stage provides for stabilization and precipitation of heavy metals. The second stage encapsulates the previously stabilized and precipitated contaminants into the crystal lattice or solid matrix of the final solidified product.
PURATEK® STABILIZATION REACTOR | FIRST STAGE
In most cases, the chemical stabilization means chemical precipitation of water-soluble inorganic contaminants, which are present in hazardous solid waste.
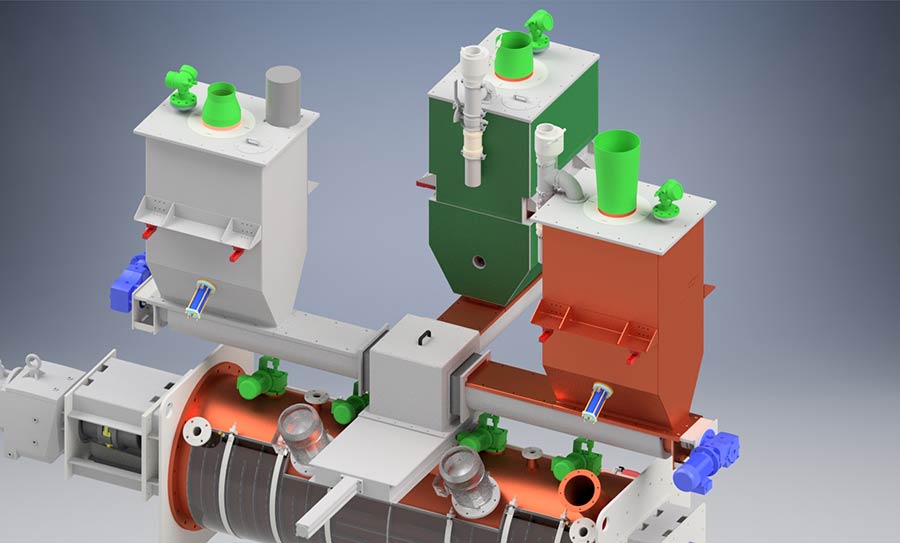
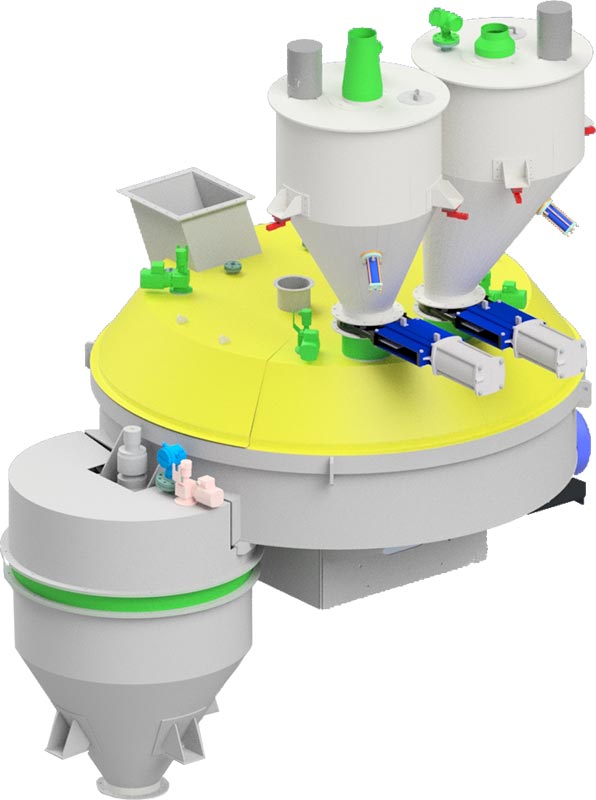
PURATEK® Stabilization & Solidification technology starts in the first reactor where chemical stabilization and precipitation takes place. The Stabilization Reactor is filled by using weighing and dosing units for solid chemo-toxic waste material or NORM waste material.
PURATEK® Weighing & Dosing units for filling up the stabilization reactor
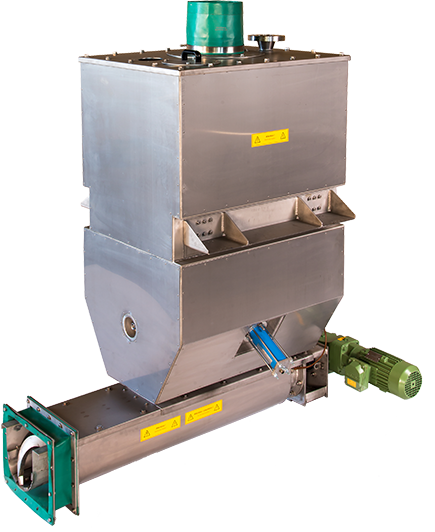
Weighing & Dosing unit for hot NORM ash, Dosing spiral conveyor with anti-wear mangan slide inserts
PURATEK® STABILIZATION REACTOR PSM 2400–2C | FIRST STAGE
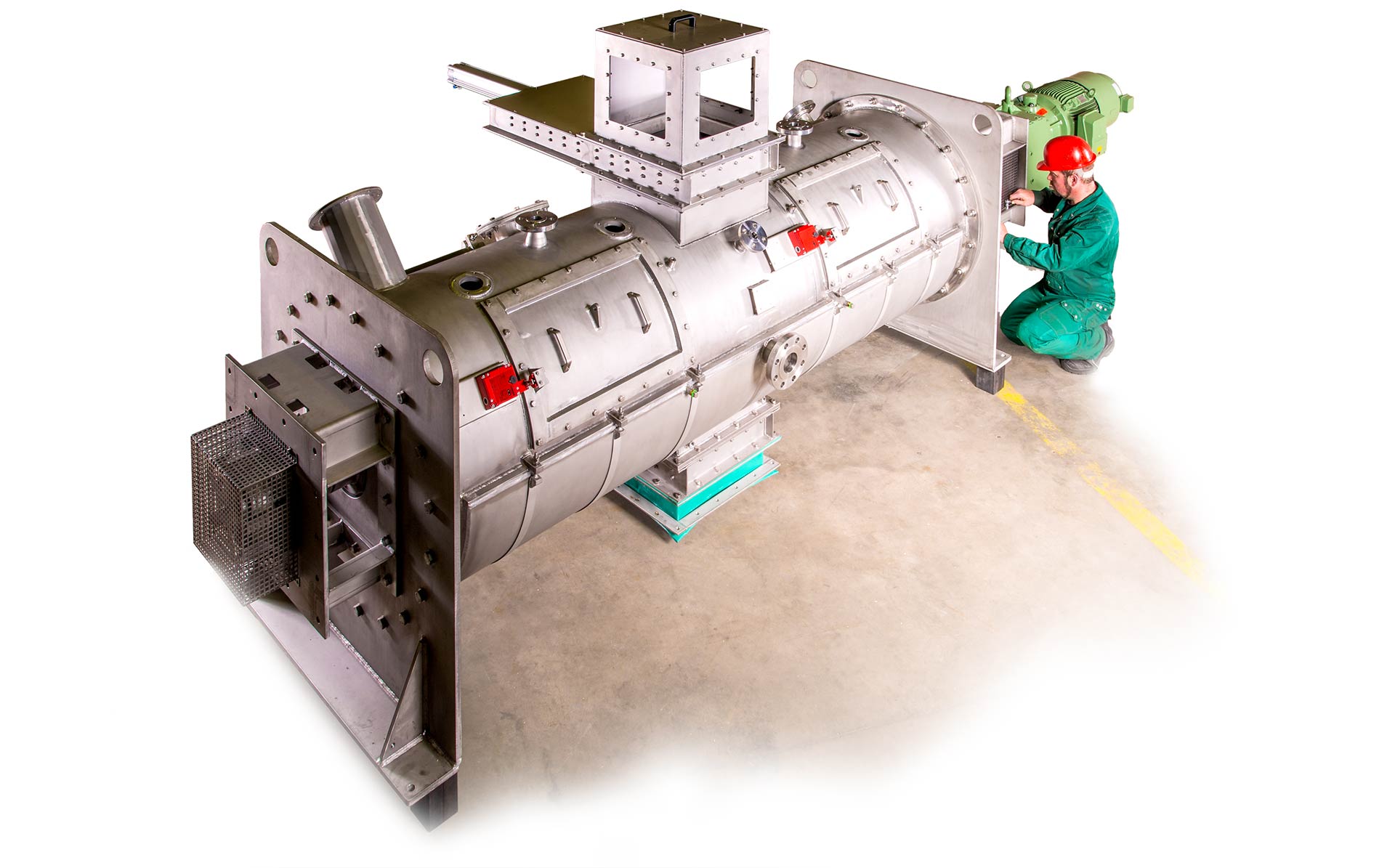

Ashes after incineration, NORM ash, scale, slag, dross and other types of chemo-toxic solid wastes, contain reactive earth alkali heavy metal oxides (BaO and RaO for example) and/ or elements of the zinc group plus cadmium and mercury. All these contaminants must be transformed into water-insoluble compounds by adding appropriate liquid chemical reagent. NORM waste requires treatment with special chemicals and technology developed by PURATEK®.
Chemical reaction between the above mentioned contaminants and the added chemicals is almost always very intensive and strong exothermic. To put chemical reaction under control, PURATEK® has designed an advanced and precise weighing and dosing system. Solid contaminates are dosed »not at once«, but gradually controlled, followed by exact injection of liquid chemicals. Chemical process is completely under control of the intelligent process controller.
PURATEK® Stabilization Reactor is specially designed for this process. As this chemical reaction runs almost always exothermic, the generated heat must be effectively dissipated. Therefore, PURATEK® Stabilization Reactor is equipped with a high performance cooling system with externally connected chiller and temperature control.
For best performing of stabilization and precipitation chemical reaction in bulk thick slurry, PURATEK® has developed and build special reactor that assures:
- intensive solid/liquid contact needed for chemical reaction
- effective dissipation of chemical reaction heat
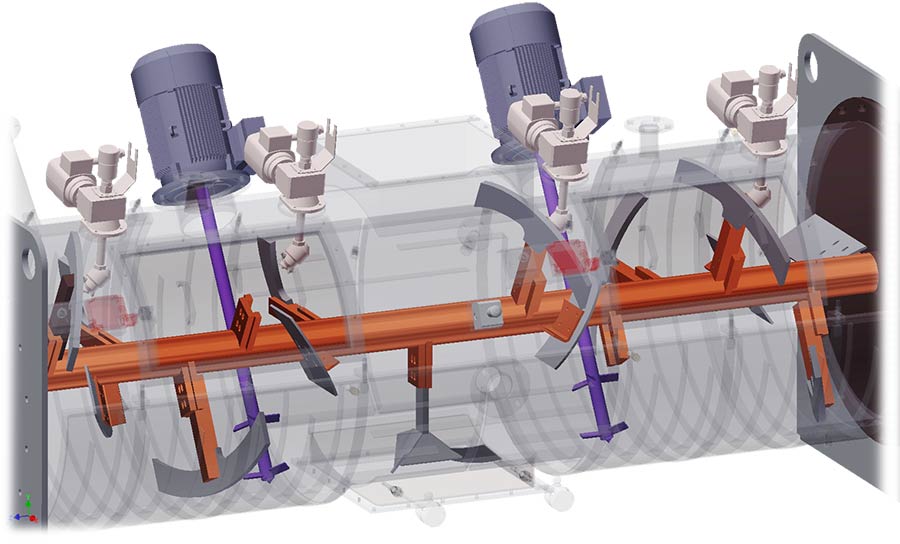
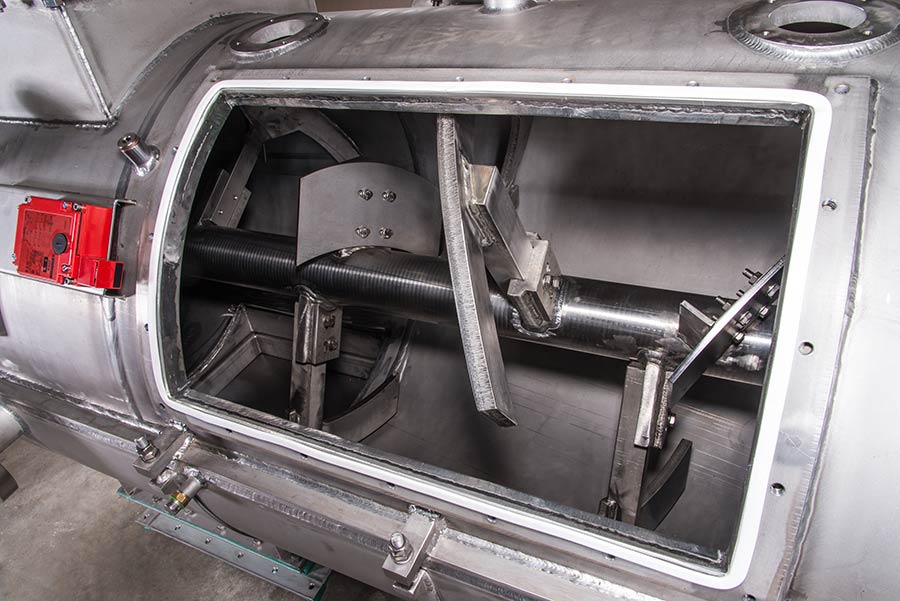
Mixing tool design
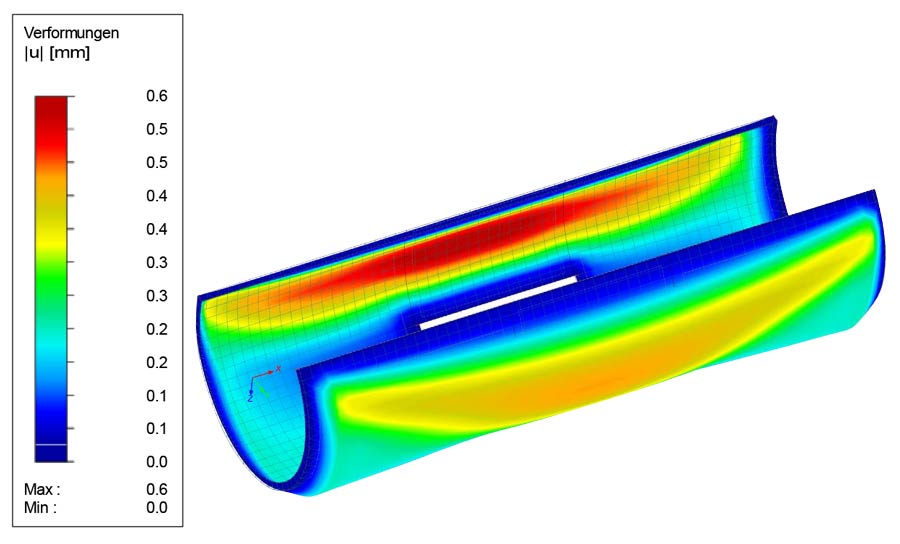
Finite Element Method (FEM) of PSM 2400 ‑2C cooling jacket — design
To meet both design requirements, PURATEK® has designed the Stabilization reactor with unique mixing fl ow characteristic and high performance heat transfer — cooling jacket.
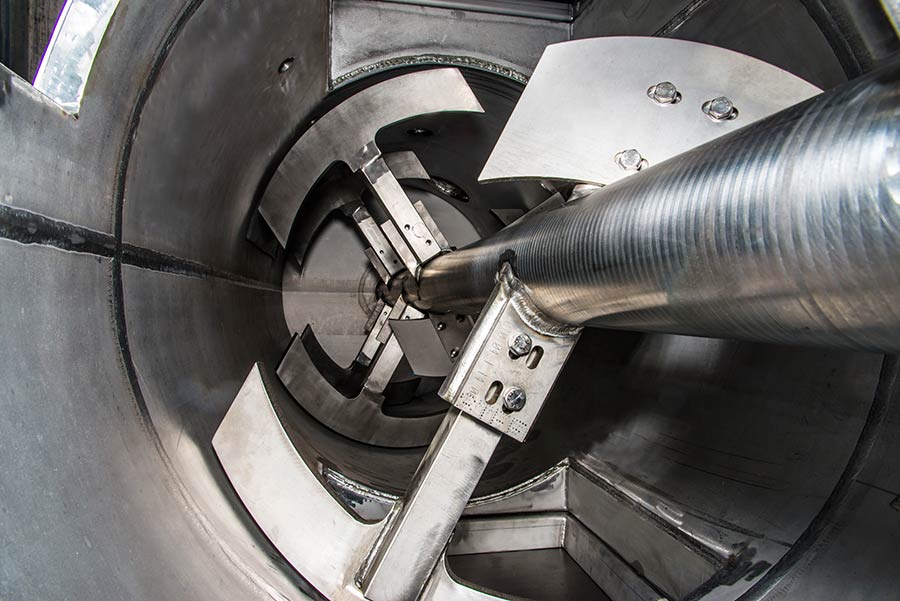
A well-dimensioned central shaft turns the heavy duty mixing tools, which perform lateral left and right bulk mixing. For micro mixing, additional two high-speed mixers are installed. They cut solid particles into pieces, increase solid/liquid interface and ensure full completion of chemical reaction. PURATEK® recommends using high chemical and abrasive resistant duplex steel for reactor fabrication material.
Ni-hardened heavy-duty mixing tools
Strong central shaft
PURATEK® STABILIZATION REACTOR PSM 2400–2C | SECOND STAGE
After the chemical stabilization and precipitation is completed, the processed material is transferred by gravity to the second reactor for further treatment.
Preparation of final solidified mixture takes place in the second reactor — special heavy-duty pan mixer, made of stainless steel, with inside lining and Ni-hardened anti-wear mixing tools, developed by PURATEK®.
Special type of chemical resistant cement, inert fillers, fine sand and recycled process water are added to the mixture to achieve the desired consistency of the final solidified product. To reduce radiation, NORM waste material requires special additives and technology developed by PURATEK®.
After curing time of the solidified mixture, the solidification process is accomplished. Compacted solidified product reaches the desired result: full encapsulation of the chemo toxic compounds in a cement-stone matrix. Conditions for safe, permanent disposal at suitable landfill are fulfilled.
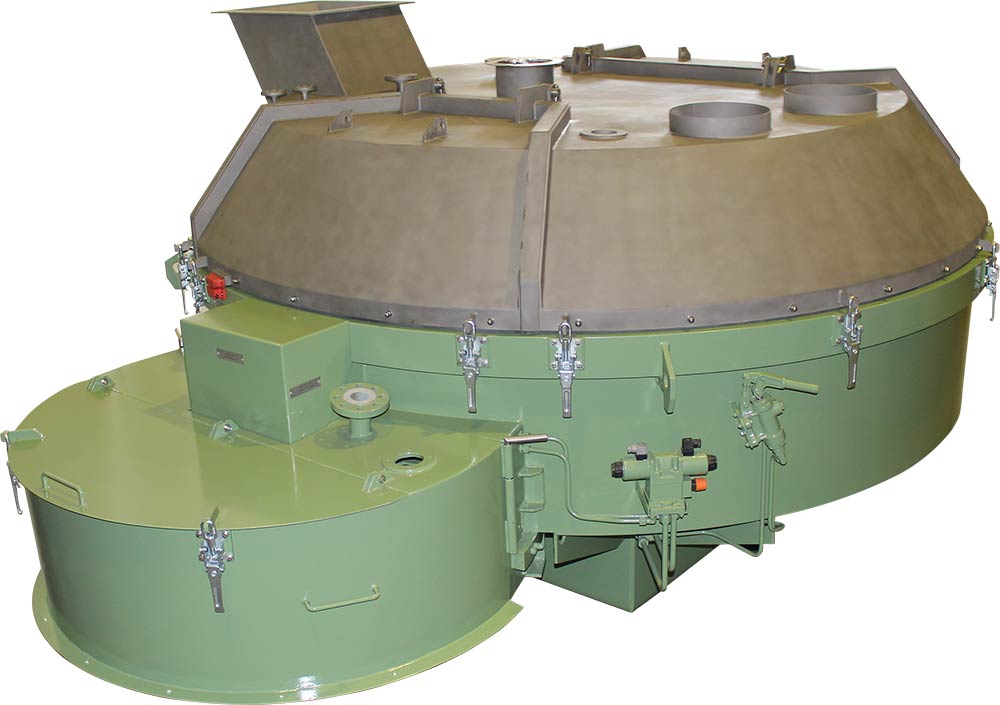

Solidification Reactor PM 2250
PURATEK® SOLIDIFICATION REACTOR HD PM 2250, WITH WEIGHING HOPPERS AND DISCHARGING FUNNEL

User-friendly operation and adjustment of the receipe trough touch-panel
The PURATEK® Stabilization & Solidification process runs fully automatically according to recipes stored in the intelligent process control unit. Specific recipes for treatment of different waste types are prepared and optimized during test operation.
PURATEK® ADVANCED HANDLING CONCEPT & LOGISTIC
The final product of the PURATEK® Stabili-zation & Solidification process is bulk-solidified mixture, which can be loaded directly on dumper truck and transported to the landfill. Another option is to cast the solidified mixture into forms/molds. In this case, the solidified mixture can be compacted additionally by means of a vibrating system. A higher quality, especially a higher comprehensive strength of the final solidified product can be achieved.
Mold walls can be removed from the ingot after a very short curing period. However, the final strength of the ingot is achieved after 30 days. The final hardened ingot shows a very low porosity, which makes water penetration impossible. Any possibility of leaching of hazardous compounds is excluded.
Hazardous solid waste should be handled and treated with a safe concept in order to avoid accidences: both, human and environmental. Safety at work is a prerequisite.
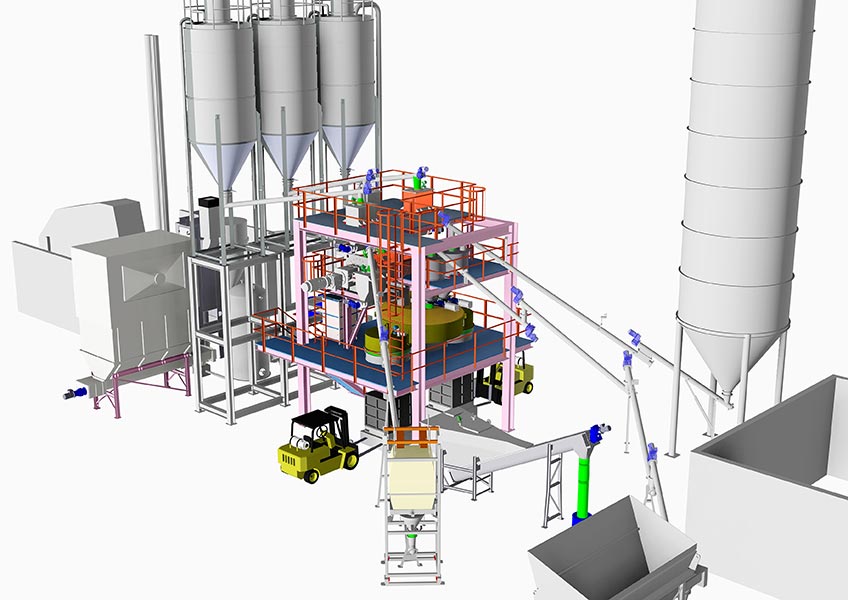
PURATEK® provides for a well-considered concept for mold handling and logistic. This includes: preparation of empty molds, transport, positioning, casting of molds, compacting, demolding, primary curing of ingots and final disposal of ingots.
According to PURATEK® handling concept, an empty form/mold is transported via a roller conveyor system under the solidified mixture discharge funnel, where vibration unit is placed. After casting and vibrating, the mold is transported via heavy-duty roller conveyor system to the primary curing area. Alternatively, forklift can be employed for the same job.
The PURATEK® Stabilization & Solidification process runs fully automatically according to recipes stored in the intelligent process control unit. Specific recipes for treatment of different waste types are prepared and optimized during test operation.
PURATEK® STABILIZATION & SOLIDIFICATION PLANT CONCEPT & LOGISTIC
The golden rule is one batch one mold, meaning that the entire content of second reactor is completely emptied into one mold. After recipe is optimization one finished batch is filled and casted exactly into one 1,0 m³ mold. For the reason of fluent handling, on the bottom of the pan mixer, there are two opposite placed hydraulic driven half-moon discharging gates, which are working alternately:
- First solidified batch goes to right gate and to right discharging funnel
- Second solidified batch goes to left gate and to left discharging funnel
Total — one mold manipulation time:
Filling one mold, vibrating one mold, removing of one casted mold by forklift, and bringing one empty mold on vibrating table is equal to twice solidification batch time.
After curing time, solidified ingots can be safely put to landfill without risk of leaching contaminants from the encapsulated and solidified waste.

PURATEK® ADVANCED HANDLING CONCEPT & LOGISTIC
NORM WASTE MATERIAL requires special handling. To prevent radiation leaking, the final NORM solidified product should be sealed with clean concrete shield.
PURATEK® recommends technical solution for casting, handling and storage of the final NORM solidified product. Radiation shielding can be achieved by using of 1.0 m³ concrete pots with integrated bottom & walls and sealed cover. Casted and waterproof sealed concrete pots with 100–120 mm walls can be safely transported and handled by PURATEK® heavy-duty carousel or roller conveyor and handled & loaded on truck by special shielded forklift.
Recommended technical solution assures effective radiation shielding and allows permanent safe storage of solidified NORM waste material on the special controlled low radiation waste depot.
APPLICATIONS FOR STABILIZATION & SOLIDIFICATION FOR WASTE TREATMENT
PURATEK® STABILIZATION & SOLIDIFICATION TECHNOLOGY WAS SUCCESSFULLY APPLIED FOR DIFFERENT TYPES OF HAZARDOUS SOLID AND CHEMO TOXIC WASTE:
- Industrial inorganic hazardous solid waste
- Bottom ash and fly ash from incineration plants
- Spent catalyst from petrochemical industry
- EAF dust from steel production
- Slag and dross from steel production
- Spent blasting materials – contaminated with heavy metals and paint
- Spent molecular sieve – contaminated with toxic chemicals
- Ash from municipal incineration plantsSpent activated alumina — contaminated with toxic chemicals
- Sludge and filter cake from Aluminum Extrusion
- Plant- high aluminum content
- Sludge from galvanizing Plant – with high heavy metals content
- Sludge from leather industry
- Chemo toxic liquid wasteContaminated soil
- Hazardous municipal waste
NORM WASTE APPLICATIONS
- NORM ash from incineration
- NORM scale from oilfield pipes contaminated with RaSO4 and RaCO3
- NORM sludge and scrapings
- NORM drilling mud
- NORM waste material in gas processing facilities
- NORM contaminated equipment
- Low radioactive material

TYPICAL CLIENTS FOR THE STABILIZATION & SOLIDIFICATION PLANT ARE:
- Waste treatment facilities
- Landfill facilities, specifically hazardous waste landfill facilities
- Hazardous waste incineration facilities
- Incineration facilities
- Municipal waste and hazardous waste incineration plants, power plants
- Waste treatment operation companies, also soil treatment companies
- Environmental service companies
- Oil drilling companies
- Refineries
- Chemical industry
- Petrochemical industry
- Metal processing industry
- Steel production industry
- Galvanizing industry
- Leather industry
- Nuclear power industry
- Disposal facilities for NORM waste
PURATEK® SCOPE OF SERVICES:
- Concept studies
- Laboratory testing
- Basic engineering, including layout of the plant
- Detail engineering
- Manufacturing of Equipment in own factory
- Delivery to site and construction / erection
- Commissioning
- Optimization of the process
- After sales service